Stem Cells
You’ve heard about stem cells in the news, and perhaps you’ve wondered if they might help you or a loved one with a serious disease. Stem cells offer great promise for new medical treatments.
What are stem cells?
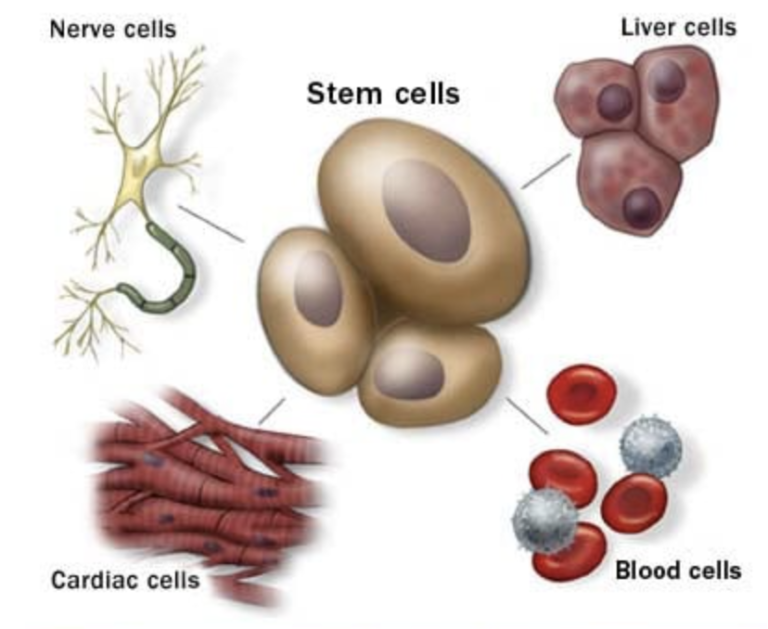
Stem cells are the body’s raw materials — cells from which all other cells with specialized functions are generated. Under the right conditions in the body or a laboratory, stem cells divide to form more cells called daughter cells.
These daughter cells become either new stem cells or specialized cells (differentiation) with a more specific function, such as blood cells, brain cells, heart muscle cells or bone cells. No other cell in the body has the natural ability to generate new cell types.
Why is there such an interest in stem cells?
Researchers hope stem cell studies can help to:
- Increase understanding of how diseases occur
- Generate healthy cells to replace cells affected by disease (regenerative medicine)
- Test new drugs for safety and effectiveness
Where do stem cells come from?
There are several sources of stem cells:
- Embryonic stem cells
- Adult stem cells
- Adult cells altered to have properties of embryonic stem cells
- Perinatal stem cells
Have stem cells already been used to treat diseases?
In stem cell transplants, stem cells replace cells damaged by chemotherapy or disease or serve as a way for the donor’s immune system to fight some types of cancer and blood-related diseases, such as leukemia, lymphoma, neuroblastoma and multiple myeloma. These transplants use adult stem cells or umbilical cord blood.
Reference Articles:
https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/bone-marrow-transplant/in-depth/stem-cells/art-20048117
Book a FREE Consultation Now
IH+ Contact Form
Contact our international team of medical professionals with language services available in English, Thai, Arabic, Chinese, Spanish, and Russian.
Please indicate your preferred language and we will do our best to accommodate your request.

